Health Education
WHAT IS CHOLERA?
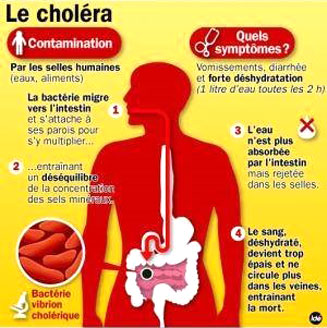
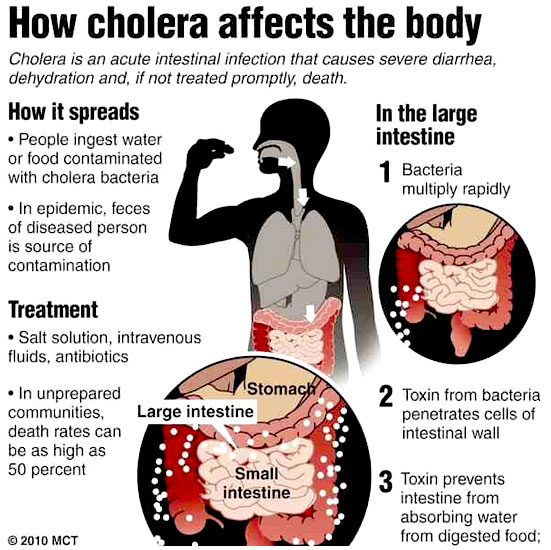
Cholera is a bacterial infection. It is caused by drinking water contaminated with vibrio cholera bacteria, or by eating food that has been in contact with contaminated water. The most common symptoms of cholera are: extensive, watery diarrhea; nausea (feeling sick); vomiting (being sick) muscle cramps.
Left untreated the combination of diarrhea and vomiting can cause a person to quickly become dehydrated (lack of fluids inside their body) and go into shock (experience a sudden massive drop in blood pressure). In the most severe cases these conditions can be fatal.
HOW CHOLERA IS SPREAD?
Around three-quarters of people who are exposed to cholera bacteria do not develop any symptoms. However, these people can contaminate water by passing stools (feces) that contain bacteria into water, or pass on the disease through poor food hygiene.
CHOLERA TREATMENT
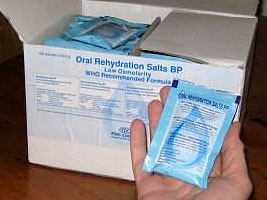
Most people, children and adults, can be treated with Oral Rehydrating Solution (ORS) as outpatients. ORS comes in small bags of powder to mix in clean water to give sugar and electrolytes to replace what is lost in diarrhea. If you don’t have prepackaged ORS, you can make an acceptable substitute with one liter of CLEAN water plus 6 – 8 teaspoons of sugar and half a teaspoon of salt.
HANDS WASHING FOR GOOD HYGIENE



LIST OF DRUGS
Chloramphenicol
Dosage & When it is to be taken: Adult: PO- The recommended dose is 50 mg/kg/day in 4 divided doses, may increase to 100 mg/kg/day in more severe infections.
Eye Drops: As 0.5% solution: Instill 1 or 2 drops 2 hourly.
How it should be taken: It comes as a tablet to take by mouth, on an empty stomach.
It also comes as eye drops to instill into the affected eyes as directed by your physician.
Warnings and Precautions: Caution should be exercised in patients with history of kidney or liver disease, bone marrow problems, any allergy, who are taking other medications, during pregnancy and breast-feeding.
Side Effects: Central Nervous System – Headache, confusion, depression, inflammation of the optic nerve and nerve inflammation.
Gastrointestinal – Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, tongue inflammation, mouth ulcer and intestinal inflammation.
Blood – Bone marrow depression and decrease in blood cell counts.
Miscellaneous – Hypersensitivity reactions such as fever, rash, shock, hives and Gray syndrome.
CHOLERA VACCINE
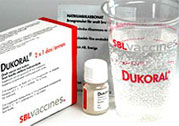
Cholera epidemic could be averted by sanitary disposal of human waste, good personal and adequate treatment of water for public consumption. While the above have been recognized as the conventional methods of controlling cholera, oral cholera vaccine use in an additional control measure.
Warning!
This vaccine does not provide 100 per cent protection against cholera. You must still follow strict food, water and personal hygiene measures to avoid the disease. These include only drinking boiled or sterilized water, avoiding ice cubes in drinks unless you know they were made from ‘safe water’, eating only freshly prepared hot food, avoiding raw fish and shell fish, and raw fruit and vegetables unless you have peeled them yourself. Measures such as these can also protect you from hepatitis A, typhoid and other types of traveler’s diarrhea. Ask your pharmacist for more advice.
Use with caution in
- HIV infection.
- People on a controlled-sodium diet (each dose contains 1.1 g sodium).
Not to be used in
- Allergy to formaldehyde.
- Acute feverish illness (you should not take the vaccine until you have recovered).
- Acute stomach or intestinal illness (you should not take the vaccine until you have recovered).
- Dukoral vaccine is not recommended for children under two years of age, as its effectiveness has not been studied in this age group.
This vaccine should not be used if you are allergic to one or any of its ingredients. Please inform your doctor or pharmacist if you have previously experienced such an allergy.
Furazolidone
Dosage & When it is to be taken:
Adults: 100mg 3-4 times. Children: 5mg/kg daily in 4 divided doses.
How it should be taken:
It comes as a tablet to take by mouth with food.
Warnings and Precautions: Caution needed for pregnant and breastfeeding women, patients with history of G6PD deficiency (genetic disorder).
Side Effects: Nausea, vomiting, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, uneasiness, rash, fever, joint pain, brown urine and anemia.
Other Precautions: Avoid excess dosage.
Storage Conditions: Store it at room temperature.
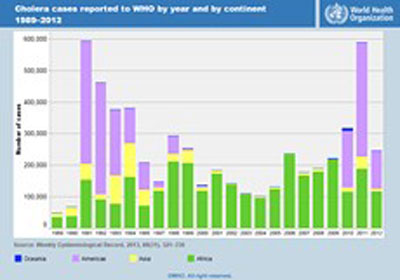
CHOLERA STATISTIC
Number of reported cholera cases